Bases
What exactly is an base? Well you're in luck if you want to find out since this page is all about the basics of bases! Let's get to it:
An base is a chemical substance or molecule that can:
An base is a chemical substance or molecule that can:
- React with and neutralize acids to form salt and water
- Turn red litmus to blue
- Turn methyl orange to yellow
- Turn phenolphthalein to purple
- Accept and neutralize hydrogen ions
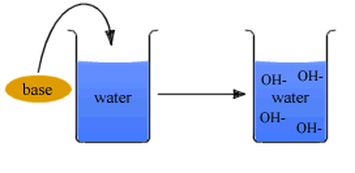
- Increase OH- ion concentration in a solution
In addition, they:
There are also 3 important theories that talk about important properties of bases. The 3 theories are summarized below but more elaborate information about all of them can be found here
1) Lewis Theory
2) Bronsted-Lowry Theory
3) Arrhenius Theory
- Are also known as alkalis if they can dissolve in water
- Have a pH above 7
- Are bitter and corrosive
- Are weak electrolytes
- Feel slippery
- Have more hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions
There are also 3 important theories that talk about important properties of bases. The 3 theories are summarized below but more elaborate information about all of them can be found here
1) Lewis Theory
- States that a base is an electron pair donor
2) Bronsted-Lowry Theory
- States that a base is a proton (hydrogen ion) acceptor
3) Arrhenius Theory
- States that bases are substances which produce hydroxide ions in a solution
From reading all about bases and alkalis previously, you might feel as if they are the same thing. However, they are not even though they are similar in many ways. The first difference is that an alkali is simply a base dissolved in water.
In addition, alkalis:
So basically you can think of it as all alkalis are bases but not all bases are alkalis.
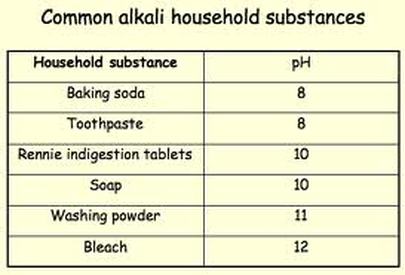
There are many different bases that can be formed. Below are some common ones and where they can be found:
In addition, alkalis:
- Are soluble in water
- Form hydroxide ions or the solution of a base in water
- Have a different structure than bases
- Have a pH over 10, rather than 7 like all bases
- Turns phenolphthalein (an indicator that you can learn more about here) from colorless to pink
So basically you can think of it as all alkalis are bases but not all bases are alkalis.
There are many different bases that can be formed. Below are some common ones and where they can be found:
Below are the uses of some common bases:
There are also many bases that we use in our everyday lives, and we don't even realize it. Below are some examples:
- Sodium Hydroxide - Makes soap, used as an oven and drain cleaner, and generates heat when combined with water
- Aluminum Hydroxide - Used in color-fast fabrics, water purification, and in antacids. Can also be a sticky gel
- Magnesium Hydroxide - Is an antacid and laxative, makes milk of magnesia when combined with water
- Calcium Hydroxide - Makes leather, mortar, and plaster, and can also lower the acidity of soil and known as caustic lime
- Ammonia - Used in multiple cleaners, fertilizers, makes rayon and nylon, but can have a smell that irritates noses and lungs
There are also many bases that we use in our everyday lives, and we don't even realize it. Below are some examples:
- Baking Soda
- Ammonia
- Lye
- Oven Cleaners
- Seawater
- Milk of Magnesia
- Soap